1. 盲點(Optic papilla, optic disk, blind spot):此處缺乏感應光線的細胞,為optic nerve 離開&central artery進入眼球的地方。
2. 黃斑(Macula lutea):上有黃色素(xanthophyll)會將藍光過濾,又無大型血管,所以透出所含黃色素的顏色,即為黃斑(yellow spot)
3. 中央凹(Central fovea):位於黃斑正中心,只含cone cell,為感光最靈敏處
4. 高度近視的人視網膜容易剝離,因其眼球結構變得較突,血液較不容易運送養分到達,單單只靠滲透是不夠的,因此最後很容易視網膜整片掉下來
5.前鉅緣(Ora serrata):位於retina最前面的構造

資料來源:ivy-rose
二、視網膜分層

資料來源:arthursclipart
最內層-->Bruch membrane是一種base membrane,為視網膜和脈絡膜之間的纖維膜。而脈絡膜則是遍布血管,提供視網膜養份
1. Pigment epithelium(色素上皮PE):
a. 單層細胞,含黑色素,構成血液網膜障壁(blood-retinal barrier),主要吸收光線
b. 色素上皮內側形成突起,與photoreceptors(感光接受器)的outer segment交錯連接,吸收感光接受器之間的光線,以避免光線反射,而增加視覺敏感度
c. 色素上皮與外側choroid layer連接緊密,與內側photoreceptors附著力較弱,易產生視網膜剝離(detachment of retina)
※choroid layer血管供應視網膜外側養分,因結締組織構造對內部供氧有限,近視度數深、過度使用眼睛、眼球老化易眼球變形,造成視網膜剝離
2. Layer of rods and cones(感光細胞層Photoreceptors,PR):
a. 光線進入retina(視網膜)映射到視網膜上的影像上下顛倒、左右相反,最後由感光接受器吸收光線後將訊號往前傳
b. Photoreceptor依形狀可分成:
桿狀細胞(Rod Cell) (bacilliform cells):微光中對光線敏感,對顏色不敏感
錐狀細胞(Cone Cells):強光才能刺激(不敏感),對顏色具敏感性
※缺乏錐狀細胞將導致色盲
c. 視網膜上的養分靠旁邊血管滲透進入,約0.4mm,薄,透明構造
基本構造:
a. outer segment(外節段):光敏感區
b. inner segment(內節段):代謝區→橢圓部(ellipsoid)富含粒線體

資料來源:加拿大麥基爾大學
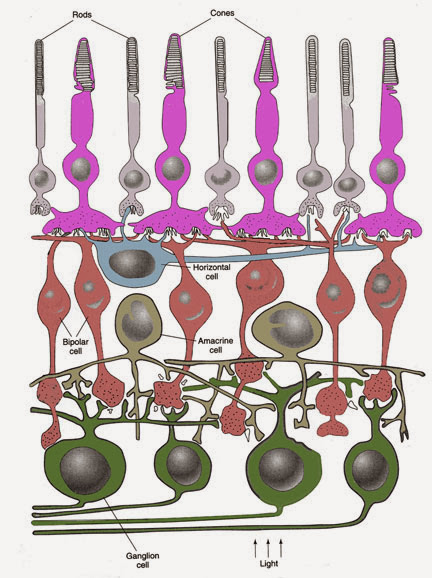
3. Outer limiting membrane(外限膜,OLM):Muller cell(神經膠細胞)的outer end,同時也是錐/桿狀細胞的inner segment與其fiber的交界
4. Outer nuclear layer(外核膜,ONL):Photoreceptor(錐/桿狀細胞)的細胞本體、細胞核所在
5. Outer plexiform layer(外叢狀層,OPL):Photoreceptor和bipolar cell形成突觸處(axon-dendryte);Horizontal cell也在這層形成突觸
6. Inner nuclear layer(內核層,INL):除錐/桿狀細胞與神經節細胞之外的細胞核都在此(雙極細胞、Amacrine cell)
Bipolar cell(雙極細胞):
a. 一級傳遞神經元,介於感光接受器與雙極細胞間
b. 一個雙極細胞接收多個桿狀細胞的訊息,但位於中央窩的一個錐狀細胞有多個雙極細胞相接
※錐狀細胞有許多雙極細胞傳至此,視覺靈敏,訊號可放大
7. Inner plexiform layer(內叢狀層IPL):
雙極細胞與神經節細胞形成突觸,Amacrine cell也在此形成突觸
8. Ganglion cell layer(神經節細胞層GCL):
a. 二級傳遞神經元,也是最早產生動作電位的細胞
b. 雙極細胞與神經節細胞的樹突和soma形成突觸,軸突穿出鞏膜,聚集形成optic nerve(髓鞘為寡樹突細胞oligodendrocyte製造)
※上述在retina內的神經都是unmyelinated
c. 神經節細胞的軸突離開鞏膜時形成的小洞稱lamina cribrosa(篩板)
資料來源:iovs
9. Nerve fiber layer(視神經纖維層)=optic fiber layer:有Ganglion cell的軸突
10. Inner limiting membrane(內限層):Muller cell的inner end,Muller cell涵蓋從外限膜至內限膜的8層
資料來源:美國斯基德莫爾大學
四、血液供應
A. 中央視網膜動脈(Central artery of rentina):由內而外供應inner part of retina。沿optic nerve進入到眼球內層。視神經(optic nerve)→視乳突(optic papilla, optic disc)→眼球→inner surface or retina→供應outer border of inner nuclear layer(注意:central artery of rentina不供應photoreceptors)
B. 脈絡叢動脈(Capillary layer of choroid):由外而內供應outer part of retina。choroid 和retina之間隔著一層由basal lamina of pigment epithelium 和inner layer of choroids形成的Bruch’s glassy membrane。而Bruch’s glassy membrane會阻礙微血管通過→養分只能藉由擴散到pigment epithelium,再到photoreceptor。因此若視網膜剝離,養分就無法到達photoreceptor
C. Cone cell 和Rod cell只能藉由兩側血液擴散得到養分。
2. 黃斑(Macula lutea):上有黃色素(xanthophyll)會將藍光過濾,又無大型血管,所以透出所含黃色素的顏色,即為黃斑(yellow spot)
3. 中央凹(Central fovea):位於黃斑正中心,只含cone cell,為感光最靈敏處
4. 高度近視的人視網膜容易剝離,因其眼球結構變得較突,血液較不容易運送養分到達,單單只靠滲透是不夠的,因此最後很容易視網膜整片掉下來
5.前鉅緣(Ora serrata):位於retina最前面的構造

資料來源:ivy-rose
二、視網膜分層

資料來源:arthursclipart
最內層-->Bruch membrane是一種base membrane,為視網膜和脈絡膜之間的纖維膜。而脈絡膜則是遍布血管,提供視網膜養份
1. Pigment epithelium(色素上皮PE):
a. 單層細胞,含黑色素,構成血液網膜障壁(blood-retinal barrier),主要吸收光線
b. 色素上皮內側形成突起,與photoreceptors(感光接受器)的outer segment交錯連接,吸收感光接受器之間的光線,以避免光線反射,而增加視覺敏感度
c. 色素上皮與外側choroid layer連接緊密,與內側photoreceptors附著力較弱,易產生視網膜剝離(detachment of retina)
※choroid layer血管供應視網膜外側養分,因結締組織構造對內部供氧有限,近視度數深、過度使用眼睛、眼球老化易眼球變形,造成視網膜剝離
2. Layer of rods and cones(感光細胞層Photoreceptors,PR):
a. 光線進入retina(視網膜)映射到視網膜上的影像上下顛倒、左右相反,最後由感光接受器吸收光線後將訊號往前傳
b. Photoreceptor依形狀可分成:
桿狀細胞(Rod Cell) (bacilliform cells):微光中對光線敏感,對顏色不敏感
錐狀細胞(Cone Cells):強光才能刺激(不敏感),對顏色具敏感性
※缺乏錐狀細胞將導致色盲
Disc 與膜的關係
|
數量
|
內含色素
|
功能
|
|
桿狀細胞
|
Disc 與膜分開成
|
漂浮狀(free-floating)
12×106較多
|
視紫質(Rhodopsin)
|
黑白視覺
暗視覺
|
錐狀細胞
|
disc 跟外膜相連
|
6×106較少
|
光視蛋白
(Photopsin)
|
彩色視覺
亮視覺
|
基本構造:
a. outer segment(外節段):光敏感區
b. inner segment(內節段):代謝區→橢圓部(ellipsoid)富含粒線體

資料來源:加拿大麥基爾大學
3. Outer limiting membrane(外限膜,OLM):Muller cell(神經膠細胞)的outer end,同時也是錐/桿狀細胞的inner segment與其fiber的交界
4. Outer nuclear layer(外核膜,ONL):Photoreceptor(錐/桿狀細胞)的細胞本體、細胞核所在
5. Outer plexiform layer(外叢狀層,OPL):Photoreceptor和bipolar cell形成突觸處(axon-dendryte);Horizontal cell也在這層形成突觸
6. Inner nuclear layer(內核層,INL):除錐/桿狀細胞與神經節細胞之外的細胞核都在此(雙極細胞、Amacrine cell)
Bipolar cell(雙極細胞):
a. 一級傳遞神經元,介於感光接受器與雙極細胞間
b. 一個雙極細胞接收多個桿狀細胞的訊息,但位於中央窩的一個錐狀細胞有多個雙極細胞相接
※錐狀細胞有許多雙極細胞傳至此,視覺靈敏,訊號可放大
7. Inner plexiform layer(內叢狀層IPL):
雙極細胞與神經節細胞形成突觸,Amacrine cell也在此形成突觸
8. Ganglion cell layer(神經節細胞層GCL):
a. 二級傳遞神經元,也是最早產生動作電位的細胞
b. 雙極細胞與神經節細胞的樹突和soma形成突觸,軸突穿出鞏膜,聚集形成optic nerve(髓鞘為寡樹突細胞oligodendrocyte製造)
※上述在retina內的神經都是unmyelinated
c. 神經節細胞的軸突離開鞏膜時形成的小洞稱lamina cribrosa(篩板)

資料來源:iovs
9. Nerve fiber layer(視神經纖維層)=optic fiber layer:有Ganglion cell的軸突
10. Inner limiting membrane(內限層):Muller cell的inner end,Muller cell涵蓋從外限膜至內限膜的8層

資料來源:美國斯基德莫爾大學
*其中在Foveola處會少掉三層:內核層(inner nuclear layer)、神經節細胞層(ganglion cell layer)和血管,因而有利於光線的集中,增強銳利度
三、視網膜細胞(Retinal cells)四、血液供應
A. 中央視網膜動脈(Central artery of rentina):由內而外供應inner part of retina。沿optic nerve進入到眼球內層。視神經(optic nerve)→視乳突(optic papilla, optic disc)→眼球→inner surface or retina→供應outer border of inner nuclear layer(注意:central artery of rentina不供應photoreceptors)
B. 脈絡叢動脈(Capillary layer of choroid):由外而內供應outer part of retina。choroid 和retina之間隔著一層由basal lamina of pigment epithelium 和inner layer of choroids形成的Bruch’s glassy membrane。而Bruch’s glassy membrane會阻礙微血管通過→養分只能藉由擴散到pigment epithelium,再到photoreceptor。因此若視網膜剝離,養分就無法到達photoreceptor
C. Cone cell 和Rod cell只能藉由兩側血液擴散得到養分。
▼感覺(sensory)
顯示/隱藏(show/hide)
標籤:
神經(nerve),
感覺(sensory)
rod cell 數量應該是12x10^7
回覆刪除可以提供一下資料的參考來源嗎? 感謝您
刪除http://askabiologist.asu.edu/rods-and-cones
刪除第3,4段落~
"Rods work at very low levels of light. We use these for night vision because only a few bits of light (photons) can activate a rod. Rods don't help with color vision, which is why at night, we see everything in a gray scale. The human eye has over 100 million rod cells.
Cones require a lot more light and they are used to see color. We have three types of cones: blue, green, and red. The human eye only has about 6 million cones. Many of these are packed into the fovea, a small pit in the back of the eye that helps with the sharpness or detail of images."