一、生理作用
1.促進肝的糖原分解和糖異生,使血糖增加
2.促進脂肪分解、過多胺基酸和加強脂肪酸氧化導致酮體生成增多---稱為糖異生可轉換額外之胺基酸成,成間單碳水化合物,並將不同形式得食物轉換成能量運用。
資料來源:維基百科
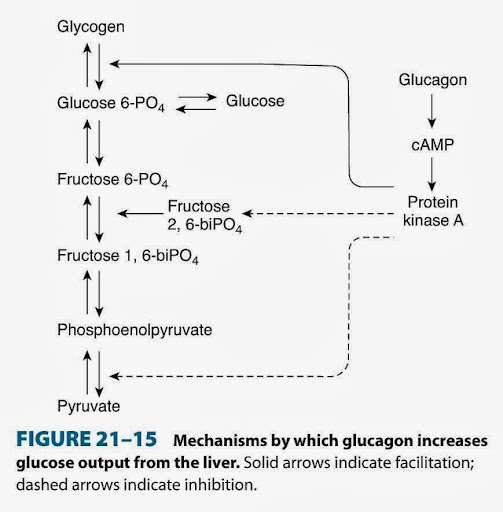
二、影響因素
1.促進因素:glucogenic amino acid, cortisol, CCK, gastrin, exercise, infection, stress
2.抑制因素:glucose, somatostatin, free fatty acid, ketones
▼消化道(Digestive tract)
顯示/隱藏(show/hide)
▼腺體(gland)
顯示/隱藏(show/hide)
0 意見:
張貼留言